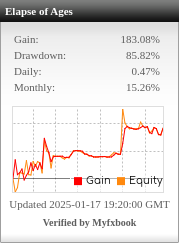
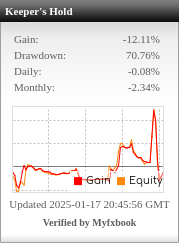
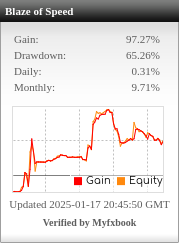
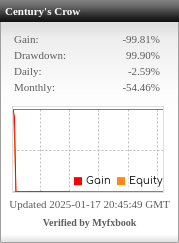
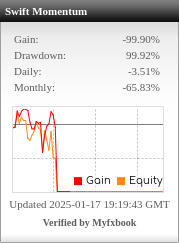
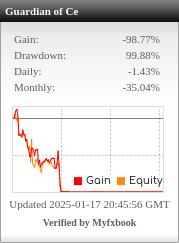
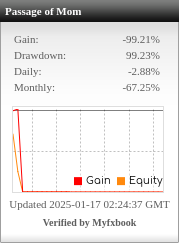
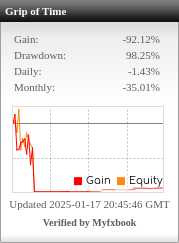
Table of Contents
You’re correct that having consistent global trading options (e.g., Friday Exit, session trading, etc.) across all strategies in your portfolio ensures better alignment and reduces potential conflicts. However, exits based on specific trade mechanics—like break-even (BE), trailing stops, partial close, or exit signals—are internal to each strategy and can add flexibility without necessarily breaking portfolio coherence. Here’s a detailed look:
1. Global Trading Options (Applied to All Strategies)
These options apply uniformly to every strategy in the portfolio and impact overall behavior. Examples include:
- Exit on Friday: Ensures no positions are held over the weekend.
- Session/Time Range Trading: Limits trading to specific hours or sessions, useful for aligning strategies with market activity.
- Minimum/Maximum Trades Per Day: Controls frequency to manage risk exposure.
Impact on Portfolio
- Consistency: All strategies adhere to the same rules, simplifying management.
- Risk Control: Reduces unpredictability from holding positions outside preferred trading windows or volatile times.
- Correlation Impact: Aligning global options can help avoid simultaneous trades that arise due to uncoordinated trading hours.
Best Practices
- Use Exit on Friday for all strategies to mitigate weekend gap risks.
- Set time ranges only if strategies target specific sessions (e.g., London Breakout).
- Avoid mixing strategies with conflicting global options (e.g., one using Friday Exit, another not).
2. Strategy-Specific Exit Mechanisms
These exits are unique to each strategy and influence trade-level performance. Examples:
- Break-Even (BE): Moves stop-loss to entry once a certain profit threshold is hit.
- Trailing Stop: Dynamically adjusts the stop-loss to lock in profits.
- Partial Close: Takes partial profit at predefined levels.
- Exit Signal: Closes the trade based on a reversal or custom indicator signal.
Impact on Portfolio
- Enhances Strategy Independence: Each strategy operates based on its internal logic, improving diversification.
- Risk Management: Advanced exits like BE and trailing stops reduce drawdowns and lock in gains.
- Potential Drawback: If exits are overly aggressive or poorly optimized, they might reduce the efficiency of profitable strategies.
Correlation Impact
Internal exits generally have minimal correlation impact unless:
- Strategies rely on identical exit logic and triggers (e.g., all use the same trailing stop settings).
- Exit signals consistently align, causing simultaneous closures across multiple strategies.
3. Combining Global Options with Internal Exits
Scenario 1: Unified Global Exit Rules
- Example: All strategies use Friday Exit, and trading is limited to 8 AM–4 PM.
- Internal Exits Allowed: BE, trailing stops, and exit signals are tuned per strategy.
- Result: Balanced portfolio with consistent risk control and flexibility in individual strategies.
Scenario 2: Diverse Internal Exits
- Example: Some strategies use aggressive trailing stops, while others rely on exit signals.
- Result: Potentially more diversified outcomes, but monitor for conflicting behaviors (e.g., strategies exiting simultaneously due to correlated conditions).
4. Recommendations
- Global Options:
- Use the same trading options (e.g., Friday Exit, session limits) across all strategies in the portfolio for consistency.
- Align global options with your trading goals (e.g., avoiding weekend gaps or managing session-specific trades).
- Internal Exits:
- Optimize exits like BE, trailing stops, and partial closes per strategy, as they are independent of portfolio-wide options.
- Avoid overly aggressive exits unless they align with the strategy’s objective (e.g., scalping).
- Correlation Check:
- Run correlation analysis after applying global options and internal exits to ensure portfolio diversification.
- If multiple strategies show high correlation, consider adjusting exits or reducing overlap in their instruments/timeframes.
Final Thought
Global trading options ensure portfolio coherence, while internal exits provide strategy-specific flexibility. As long as global rules are harmonized and internal exits are carefully optimized, they won’t negatively impact the portfolio’s overall performance. Would you like a deeper dive into optimizing these exit strategies or analyzing correlations?